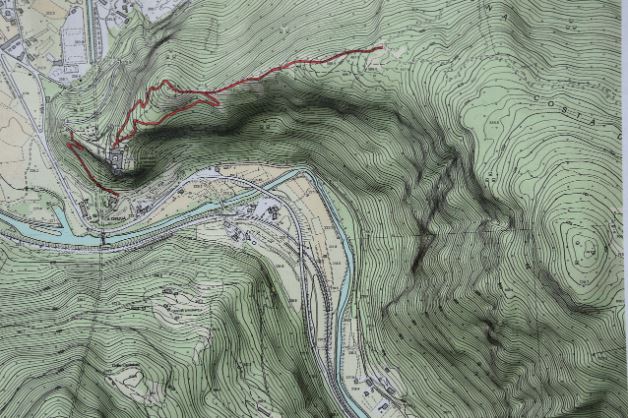
A topographic map is a type of map that shows the physical features and elevation changes of a land area. Unlike regular maps, topographic maps provide a detailed representation of the terrain and its features. These maps are commonly used by hikers, campers, and outdoor enthusiasts to navigate through unfamiliar terrain. However, they are also used by scientists, geographers, and engineers to understand the landscape and its features.
Topographic maps are created by taking measurements of the land’s surface using specialized instruments such as surveying equipment, aerial photography, and satellite imagery. These measurements are then used to create a detailed and accurate representation of the terrain. The map typically includes contour lines, which show the elevation changes of the land, as well as symbols and colors that represent physical features such as rivers, lakes, forests, and mountains.
Topographic maps are an essential tool for anyone who wants to understand the landscape around them. They provide valuable information about the terrain, such as the steepness of a slope, the location of water sources, and the type of vegetation present in an area. With this information, hikers and outdoor enthusiasts can plan their routes and prepare for their trips accordingly.
Characteristics of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps have several unique characteristics that set them apart from other types of maps. One of the most distinctive features of a topographic map is the use of contour lines. Contour lines are the curved lines that appear on the map, and they represent the elevation changes of the land. The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the terrain.
Another characteristic of topographic maps is the use of symbols and colors to represent physical features. For example, blue lines on the map represent rivers and streams, while green areas represent forests and other vegetation. Brown areas on the map represent areas with little or no vegetation, such as deserts or rocky terrain.
Topographic maps also include a scale and a datum, which are used to measure distances and locations accurately. The scale indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground. The datum is a reference point used to locate features on the map accurately.
How Topographic Maps are Created
Topographic maps are created using various methods, including surveying, aerial photography, and satellite imagery. Surveying involves taking measurements of the land’s surface using specialized instruments such as theodolites, total stations, or GPS receivers. These measurements are then used to create a detailed and accurate representation of the terrain.
Aerial photography is another method used to create topographic maps. This involves taking photographs of the land from an aircraft or drone. The photographs are then analyzed and used to create a detailed representation of the terrain.
Satellite imagery is also used to create topographic maps. This involves using satellite data to create a digital model of the terrain. The model is then used to create a detailed and accurate representation of the land’s surface.
Once the data has been collected, it is compiled and used to create the topographic map. The map typically includes contour lines, symbols, and colors that represent physical features, as well as a scale and datum.
Uses of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps have a wide range of uses, from navigation to scientific research. Outdoor enthusiasts such as hikers, campers, and hunters use topographic maps to navigate through unfamiliar terrain. The maps provide valuable information about the terrain, such as the location of water sources, the type of vegetation present in an area, and the steepness of a slope.
Scientists and geographers use topographic maps to study the land’s surface and its features. They use the maps to analyze the terrain, identify geological features, and study the impacts of natural disasters such as landslides and earthquakes.
Engineers also use topographic maps to plan and design infrastructure projects such as roads, bridges, and buildings. The maps provide valuable information about the terrain, such as the elevation changes and the location of water sources, which can be used to design structures that are safe and functional.
Symbols and Colors on Topographic Maps
Topographic maps use symbols and colors to represent physical features on the land’s surface. These symbols and colors provide valuable information about the terrain and its features. Some of the most common symbols used on topographic maps include:
- Contour lines, which show the elevation changes of the land
- Blue lines, which represent rivers and streams
- Green areas, which represent forests and other vegetation
- Brown areas, which represent areas with little or no vegetation
- Black dots, which represent man-made features such as buildings or bridges
The colors used on topographic maps also provide valuable information about the terrain. For example, blue areas on the map represent bodies of water, while brown areas represent areas with little or no vegetation.
Understanding Contour Lines on Topographic Maps
Contour lines are one of the most important features of a topographic map. They show the elevation changes of the land and provide valuable information about the terrain. Understanding contour lines is essential for anyone who wants to use a topographic map for navigation or scientific research.
Contour lines are curved lines that appear on the map. Each contour line represents a specific elevation, and the distance between the lines indicates the steepness of the terrain. The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the terrain.
Contour lines can also be used to identify features such as hills, valleys, and ridges. For example, a hill is represented by a series of concentric contour lines that form a circle. The highest point of the hill is located at the center of the circle, and the elevation decreases as you move away from the center.
Scale and Datum on Topographic Maps
The scale and datum are two essential components of a topographic map. The scale indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground. For example, a scale of 1:24,000 means that one inch on the map represents 24,000 inches on the ground.
The datum is a reference point used to locate features on the map accurately. There are several different datums used in mapping, depending on the region and the purpose of the map. The most common datum used in the United States is the North American Datum of 1983 (NAD83).
Understanding the scale and datum is essential for anyone who wants to use a topographic map for navigation or scientific research. Without an accurate scale and datum, it is impossible to measure distances or locate features on the map accurately.
Topographic Map Vs. Other Types of Maps
Topographic maps differ from other types of maps in several ways. Unlike road maps or political maps, topographic maps provide a detailed representation of the terrain and its features. They show the physical features of the land, such as mountains, valleys, and rivers, as well as the elevation changes of the terrain.
Topographic maps are also different from satellite maps or aerial photographs. While these maps provide a detailed view of the land’s surface, they do not show the elevation changes or other physical features of the terrain. Topographic maps are essential for anyone who wants to understand the landscape and its features, whether for navigation, scientific research, or engineering projects.
Conclusion
Topographic maps are an essential tool for anyone who wants to understand the landscape around them. They provide valuable information about the terrain, such as the location of water sources, the type of vegetation present in an area, and the steepness of a slope. With this information, hikers and outdoor enthusiasts can plan their routes and prepare for their trips accordingly. Scientists, geographers, and engineers also use topographic maps to study the land’s surface and its features. Understanding the characteristics of topographic maps, how they are created, and how to use them is essential for anyone who wants to explore the world around them.


