The terrestrial hydrosphere is a system of water that includes all the water on Earth, from groundwater to surface water and atmospheric water vapor. The hydrosphere plays an essential role in regulating the Earth’s climate, supporting life, and shaping the landscape we see around us. Understanding the hydrosphere is crucial for anyone interested in environmental science, geography, or climate change. In this article, we’ll explore the function and components of the terrestrial hydrosphere, from the oceans and rivers to the water cycle and the role of humans in shaping this vital resource.
The Function of the Hydrosphere
The function of the hydrosphere is to transport and distribute heat around the Earth, regulate the planet’s climate, transport nutrients and minerals, and provide a habitat for aquatic organisms. The hydrosphere also plays an essential role in shaping the Earth’s landscape, eroding rocks, and creating landforms such as valleys, canyons, and deltas.
One of the primary functions of the hydrosphere is to regulate the Earth’s climate. Water has a high heat capacity, which means it takes a lot of energy to raise its temperature. As a result, the ocean acts as a giant heat sink, absorbing heat during warm periods and releasing it during cooler periods. This helps to regulate the Earth’s temperature, preventing it from getting too hot or too cold.
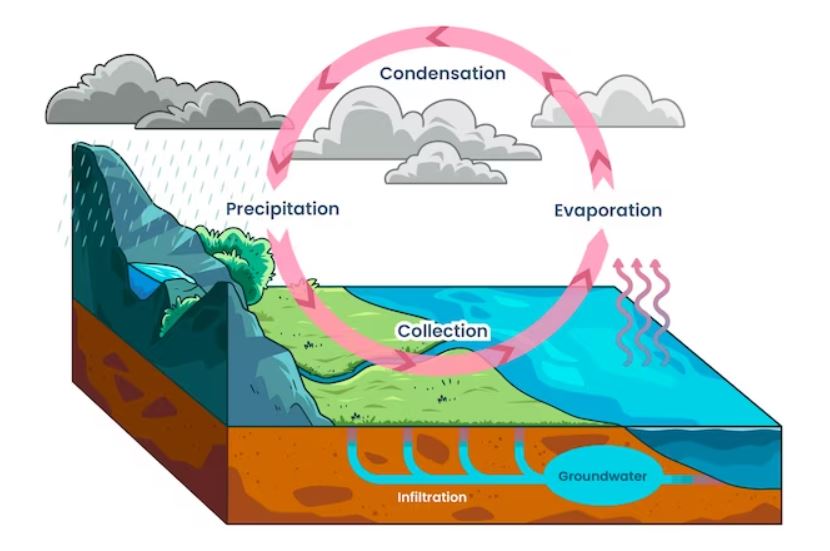
The hydrosphere also plays a crucial role in the water cycle, which is the process by which water is circulated the Earth. The water cycle involves the evaporation of water from the surface of the Earth, the formation of clouds, and the precipitation of water back onto the Earth’s surface. This cycle helps to distribute water around the planet, ensuring that all living organisms have access to the water they need to survive.
Components of the Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere is made up of several components, including oceans, lakes, rivers, and groundwater. The oceans are the largest component of the hydrosphere, covering about 71% of the Earth’s surface. They play a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate, absorbing heat and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Lakes and rivers are another essential component of the hydrosphere. They provide habitats for aquatic organisms and serve as a source of freshwater for human use. Groundwater is water that is stored beneath the Earth’s surface in aquifers. It is an essential source of freshwater, and many communities rely on it for their drinking water.
The atmosphere is also a component of the hydrosphere, as it contains water vapor. The water vapor in the atmosphere plays an essential role in the water cycle, as it is the source of precipitation.
Importance of the Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere is essential for maintaining the Earth’s ecosystem, regulating the planet’s climate, and supporting human life. The hydrosphere provides habitats for aquatic organisms, which form the base of many food chains. It also plays a critical role in regulating the Earth’s temperature, preventing it from getting too hot or too cold.
The hydrosphere is also essential for human use. It provides freshwater for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use. The oceans are an essential source of seafood and provide transportation routes for goods around the world.
Natural and Human-Induced Changes to the Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere is constantly changing due to natural and human-induced factors. Natural factors include climate change, which can affect the amount of precipitation and the temperature of the ocean. Natural disasters, such as floods and hurricanes, can also have a significant impact on the hydrosphere.
Human-induced changes to the hydrosphere include pollution, overuse of freshwater resources, and climate change. Pollution from agricultural and industrial activities can contaminate freshwater and harm aquatic organisms. Overuse of freshwater resources can lead to depletion of aquifers and water scarcity in some regions.
Climate change is also having a significant impact on the hydrosphere. Rising temperatures are causing melting of glaciers and ice caps, which is contributing to sea-level rise. Changes in precipitation patterns are also affecting the distribution of freshwater resources.
Challenges Facing the Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere is facing several challenges that threaten its ability to support life and provide freshwater for human use. Pollution, overuse of freshwater resources, and climate change are all significant challenges that need to be addressed.
Pollution from agricultural and industrial activities is a significant problem, as it can contaminate freshwater resources and harm aquatic organisms. Overuse of freshwater resources can lead to depletion of aquifers and water scarcity in some regions. Climate change is also having a significant impact on the hydrosphere, causing sea-level rise and changes in precipitation patterns.
Ways to Protect the Hydrosphere
There are several ways to protect the hydrosphere, including conservation, sustainable use, and policy changes. Conservation efforts can include protecting wetlands and other habitats for aquatic organisms. Sustainable use of freshwater resources can involve using water-efficient technologies and reducing water waste.
Policy changes can also help protect the hydrosphere. Governments can implement regulations to reduce pollution from industrial and agricultural activities. They can also work to improve water management and promote sustainable use of freshwater resources.
Future of the Hydrosphere
The future of the hydrosphere is uncertain, as it is facing several significant challenges. However, technological advancements and innovative solutions offer hope for the future. For example, new technologies are being developed to improve water efficiency and reduce pollution from industrial and agricultural activities.
Innovative solutions, such as desalination, can provide a source of freshwater for regions that are experiencing water scarcity. However, these solutions may come with their own set of environmental challenges, and it is essential to consider the long-term impacts of any new technologies or solutions.
Conclusion
The hydrosphere is a critical component of our planet’s ecosystem, regulating the Earth’s climate, supporting life, and shaping the landscape we see around us. However, it is facing several significant challenges, including pollution, overuse of freshwater resources, and climate change.
Protecting the hydrosphere is essential for maintaining the Earth’s ecosystem and providing freshwater for human use. Conservation, sustainable use, and policy changes can all help to protect this vital resource. By working together to address these challenges, we can ensure that the hydrosphere continues to support life on Earth for generations to come.


