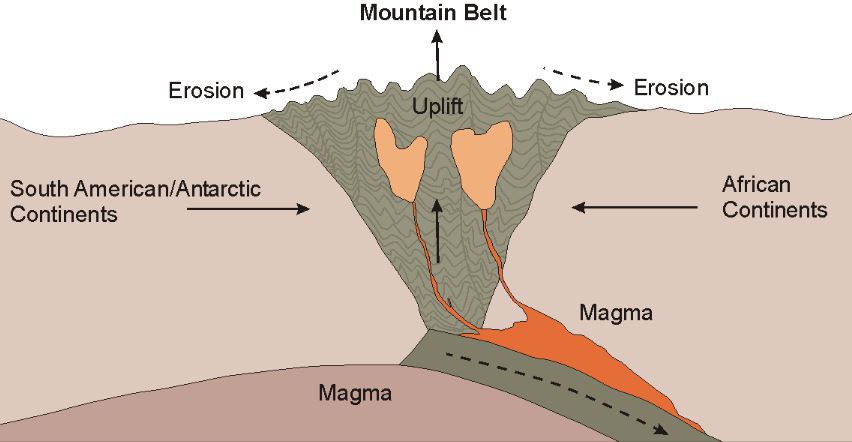
Orogeny is a geological process by which mountain ranges are formed through tectonic plate movements and collisions. This process involves the folding, faulting, and uplifting of rock layers over millions of years, resulting in the majestic mountain landscapes we see today. The word “orogeny” comes from the Greek words “oros,” meaning mountain, and “genesis,” meaning creation.
The process of orogenesis is a complex one that involves the movement of tectonic plates. When two plates collide, one plate is subducted, or pushed, beneath the other plate. This causes the rock layers to fold and buckle, forming mountain ranges. The movement of the plates can also cause sections of rock to be pushed up and over other sections, creating faults and thrusts. The process of orogeny can take millions of years, and the resulting mountain ranges can be thousands of feet tall.
Orogeny is an important process in geology because it helps us understand the history of the Earth’s crust and the forces that have shaped it over time. By studying the characteristics of orogeny, geologists can gain insight into the geological processes that have occurred in the past and those that may occur in the future.
The different types of orogeny
There are several different types of orogeny, each with its own characteristics and processes. One type of orogeny is collisional orogeny, which occurs when two tectonic plates collide. When this happens, the plates can buckle and fold, creating mountain ranges. Another type of orogeny is extensional orogeny, which occurs when tectonic plates pull apart. This can create rift valleys and other geological features.
Another type of orogeny is compressional orogeny, which occurs when tectonic plates move towards each other. This can cause the rock layers to fold and fault, creating mountain ranges. Transform orogeny is another type of orogeny, which occurs when tectonic plates slide past each other. This can cause the formation of faults and other geological features.
Each type of orogeny has its own unique characteristics and processes, and studying these can help us understand how mountain ranges are formed and how the Earth’s crust has evolved over time.
The characteristics of orogeny
One of the main characteristics of orogeny is the formation of faults. When tectonic plates collide or move apart, the rock layers can be pushed up and over each other, creating faults. These faults can cause earthquakes and other geological disturbances.
Another characteristic of orogeny is the movement of rock layers. As the tectonic plates move, the rock layers can be folded and pushed up, creating mountain ranges. This can also cause the formation of thrusts and folds in the rock layers.
The formation of folds is another characteristic of orogeny. When the rock layers are pushed up and over each other, they can fold and buckle, creating geological features such as synclines and anticlines. These folds can also be involved in the formation of thrust faults.
The process of orogeny can take millions of years, and the resulting mountain ranges can be thousands of feet tall. Understanding the characteristics of orogeny is essential for geologists, as it helps them to decipher the history of the Earth’s crust and the forces that have shaped it over time.
The factors that influence orogeny
Several factors can influence the process of orogeny. One of the main factors is the type of tectonic plate boundary. When two plates collide, for example, the resulting orogeny will be different from that which occurs when two plates move apart.
The thickness and composition of the rock layers can also influence orogeny. If the rock layers are thick and strong, they may be able to resist deformation and buckling. If they are thin and weak, they may be more likely to fold and fault.
The temperature and pressure of the rock layers can also influence orogeny. If the rock layers are hot and under high pressure, they may be more likely to deform and buckle. If they are cold and under low pressure, they may be more likely to fracture and fault.
Other factors that can influence orogeny include the speed and direction of the tectonic plate movement, the presence of fluids in the rock layers, and the presence of pre-existing geological features.
Examples of orogeny around the world
There are many examples of orogeny around the world, each with its own unique characteristics and processes. One famous example is the Himalayas, which were formed by the collision of the Indian Plate with the Eurasian Plate. This collision caused the rock layers to fold and fault, creating the towering mountain range we see today.
Another example of orogeny is the Appalachian Mountains in the eastern United States. These mountains were formed through a combination of collisional and compressional orogeny, as tectonic plates collided and pushed up the rock layers.
The Rocky Mountains in western North America were formed through a combination of compressional and extensional orogeny. The movement of tectonic plates caused the rock layers to fold and fault, creating the rugged mountain landscape we see today.
The impact of orogeny on the Earth’s surface
The process of orogeny has had a significant impact on the Earth’s surface. The formation of mountain ranges has created unique habitats for plants and animals, and has helped to shape the climate and weather patterns in different regions.
Orogeny has also had an impact on human civilization. Mountain ranges have provided natural barriers and defense systems, as well as resources such as minerals and water. The study of orogeny is essential for understanding the geological and environmental factors that have shaped human history.
Understanding the importance of orogeny in geology
In conclusion, orogeny is a fascinating process by which mountain ranges are formed through tectonic plate movements and collisions. The characteristics of orogeny include the formation of faults, the movement of rock layers, and the formation of folds and thrusts.
Understanding orogeny is essential for geologists, as it helps them to decipher the history of the Earth’s crust and the forces that have shaped it over time. By studying the different types of orogeny, the factors that influence its processes, and the examples of orogeny around the world, we can gain a deeper understanding of this remarkable geological process and its impact on the Earth’s surface.


