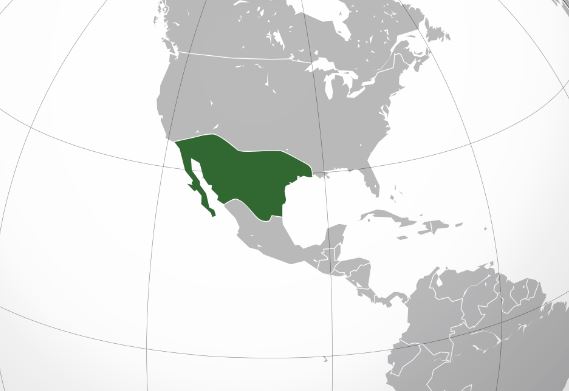
Aridoamerica is a region located in the central and northern parts of Mexico, spanning a diverse range of landscapes and cultures. The region is characterized by its arid and semi-arid climate, which has shaped the flora, fauna, and human settlements that call it home. In this article, we will explore what makes Aridoamerica special and different from other regions in Mexico and beyond.
Geographical location and climate
Aridoamerica is located in the central and northern parts of Mexico, covering an area of approximately 500,000 square kilometers. The region is bordered by Mesoamerica to the south, Oasisamerica to the northwest, and the Sierra Madre Occidental and Sierra Madre Oriental mountain ranges to the east and west, respectively.
The climate in Aridoamerica is characterized by hot and dry summers and mild winters. The region receives very little rainfall throughout the year, with an average of less than 500 millimeters per year. This arid and semi-arid climate has shaped the landscape of the region, which is dominated by deserts, grasslands, and scrublands.
Characteristics of Aridoamerica
Aridoamerica is home to a wide range of plant and animal species that have adapted to the arid conditions of the region. The most common plant species include cacti, yuccas, and mesquites, while the most common animal species include rodents, reptiles, and birds.
Human settlements in Aridoamerica are often concentrated around oases and rivers, where water is more abundant. These settlements range from small, nomadic groups to larger, sedentary communities that engage in agriculture and trade. The traditional cultures of Aridoamerica have a strong emphasis on survival and adaptation to the harsh conditions of the region.
Comparison with Mesoamerica and Oasisamerica
While Aridoamerica shares some similarities with neighboring regions, such as Mesoamerica and Oasisamerica, it also has its own unique characteristics and cultural traditions.
Mesoamerica, located to the south of Aridoamerica, is characterized by a much wetter climate and a more diverse range of plant and animal species. Mesoamerican cultures were known for their advanced agricultural practices, complex social hierarchies, and monumental architecture, such as the pyramids of the Aztecs and Maya.
Oasisamerica, located to the northwest of Aridoamerica, is characterized by its reliance on oases and other sources of water in an otherwise arid landscape. The cultures of Oasisamerica were known for their trading networks, which spanned across the deserts and mountains of the region.
Aridoamerican cultures and their impact
Aridoamerica is home to a diverse range of traditional cultures, each with its own unique customs and traditions. Some of the most well-known Aridoamerican cultures include the Chichimecas, Tarahumaras, and Yaquis.
The Chichimecas were a group of nomadic tribes that lived in the northern parts of Aridoamerica. They were known for their resistance to Spanish colonization and their use of the bow and arrow in warfare.
The Tarahumaras, also known as the Rarámuri, are a sedentary culture that lives in the mountains of northern Mexico. They are known for their long-distance running abilities and their use of the foot as the primary mode of transportation.
The Yaquis are a culture that lives in the southern parts of Aridoamerica, near the border with the United States. They are known for their resistance to Spanish colonization and their use of the bow and arrow in warfare.
These traditional cultures have had a significant impact on the history and development of Aridoamerica, influencing everything from the region’s architecture and art to its modern-day politics and social structures.
Pre-Columbian history of Aridoamerica
Before the arrival of the Spanish in the 16th century, Aridoamerica was home to a number of advanced civilizations and cultures. These included the Anasazi, Hohokam, and Mogollon cultures, which were known for their advanced agricultural practices, monumental architecture, and intricate social hierarchies.
One of the most well-known pre-Columbian cultures of Aridoamerica was the Teotihuacan culture, which flourished from the 2nd to the 8th century AD. The Teotihuacan people built a complex urban center that was characterized by monumental architecture, including the Pyramid of the Sun and the Pyramid of the Moon.
Another important pre-Columbian culture of Aridoamerica was the Toltec culture, which flourished from the 9th to the 12th century AD. The Toltecs were known for their military prowess, their advanced metallurgy, and their complex social hierarchies.
Modern Aridoamerica
Today, Aridoamerica is a region that faces a number of challenges and opportunities. The region is home to a growing population that faces issues such as poverty, unemployment, and water scarcity.
Despite these challenges, Aridoamerica is also a region that is rich in natural resources and cultural heritage. The region’s mining industry, for example, has become an important source of economic growth and development.
Tourism is also an important industry in Aridoamerica, with visitors coming to explore the region’s diverse landscapes, cultural heritage, and traditional crafts. The region’s traditional crafts, such as pottery, weaving, and basketry, are known for their intricate designs and use of natural materials.
Challenges and opportunities in Aridoamerica
One of the biggest challenges facing Aridoamerica is water scarcity. The region receives very little rainfall, and its rivers and aquifers are often over-exploited. This has led to a number of environmental problems, including soil erosion, desertification, and loss of biodiversity.
Another challenge facing Aridoamerica is poverty. Many of the region’s communities are marginalized and lack access to basic services such as healthcare and education. This has led to a number of social and economic problems, including high rates of unemployment and crime.
Despite these challenges, there are also opportunities for growth and development in Aridoamerica. The region’s natural resources, such as its minerals and natural gas reserves, offer the potential for economic growth and development. The region’s traditional crafts and cultural heritage also offer opportunities for tourism and cultural exchange.
Aridoamerica in popular culture
Aridoamerica has been the subject of numerous works of literature, film, and music. These works often explore the region’s landscapes, cultures, and history, and have helped to raise awareness of the region’s unique characteristics and significance.
One of the most well-known works of literature set in Aridoamerica is Cormac McCarthy’s “Blood Meridian”. The novel tells the story of a teenage runaway who joins a group of scalp hunters in the 1850s. The novel is known for its stark portrayal of violence and the barren landscapes of Aridoamerica.
Conclusion
Aridoamerica is a region that is rich in history, culture, and natural beauty. The region’s arid and semi-arid climate has shaped its landscapes, flora, fauna, and human settlements, creating a unique and diverse region that is unlike any other in Mexico or beyond.
While Aridoamerica shares some similarities with neighboring regions such as Mesoamerica and Oasisamerica, it also has its own unique characteristics and traditions. These traditions have had a significant impact on the history and development of Aridoamerica, influencing everything from the region’s art and architecture to its modern-day politics and social structures.
Despite the challenges facing Aridoamerica, the region also offers opportunities for growth and development, from its natural resources to its traditional crafts and cultural heritage. By exploring the wonders of Aridoamerica, we can gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating and often-overlooked part of the world.


